Boosting ML with Rust: High Performance and Reliability with a Neural Network Example
In the universe of Data Science and Machine Learning 🤖, the Python 🐍 language has been widely adopted, offering an extensive ecosystem of libraries and tools that drive research and development in this field.
However, in the quest to improve the performance and reliability of ML models, I came across the Rust 🦀 language, known for its exceptional execution speed, robust memory management, and support for parallelism. This discovery piqued my curiosity, leading me to explore the possibilities of using Rust as an alternative to scale Machine Learning projects and achieve high performance 🚀.

Image from Unsplash by Raphael Renter
The Potential of Rust in Machine Learning
As I began my studies in Rust, I quickly realized that its security and performance features could be highly advantageous for developing Machine Learning models in production environments. While Python is widely adopted in the ML community, Rust offers a unique approach, focused on security without compromising speed.
The feared and “annoying” 😠 Rust compiler becomes a valuable ally, preventing us from creating code with potential issues. The emphasis on concepts like “ownership” and “borrowing” in Rust helps avoid common errors, such as invalid references and memory leaks, providing greater reliability to models and facilitating code debugging.
Machine Learning Ecosystem in Rust
It is true that the Machine Learning ecosystem in Rust is still developing and has not yet reached the breadth of Python’s ecosystem. However, there are already emerging libraries and tools that can be crucial for those wishing to explore this approach.
One standout library is tch-rs, which provides access to the PyTorch API for Rust. This library enables the construction 📦 and training of Deep Learning models in a safer and faster programming language. By harnessing the power of PyTorch along with Rust’s efficiency, it is possible to develop Machine Learning models that combine high performance with reliability.
Example of Creating a NN for MNIST Digit Classification
To illustrate Rust’s potential in Machine Learning, this article will present a practical example of creating a neural network 🧠 for classifying digits in the MNIST dataset. The MNIST dataset consists of 28x28 grayscale images of handwritten digits (0 to 9). Our goal will be to train the neural network to correctly classify these digits.
Installation and Configuration
Before proceeding, it is essential to ensure that Rust is installed on your system, along with the build-essential packages that contain the necessary compilation programs. The tests were done using a Linux 🐧 machine.
1. Download the project from Git 🛠️
git clone https://github.com/NeuroQuestAi/rust-nn.git && cd rust-nn2. Torch 💻
The torch version used was version v2.0.0. You can download it directly from the website https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/, or follow the procedures below via the command line. Package used: (libtorch-cxx11-abi-shared-with-deps-2.0.0+cu118.zip).
In the root folder of the project, create a libs directory:
mkdir libsNow download the Torch lib and unzip it:
curl -L "https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/cu118/libtorch-cxx11-abi-shared-with-deps-2.0.0%2Bcu118.zip" libs/libtorch-cxx11-abi-shared-with-deps-2.0.0+cu118.zipThe package is about 2.3 GB. Now unzip the file:
unzip libs/libtorch-cxx11-abi-shared-with-deps-2.0.0+cu118.zip -d libs/Now it is necessary to export the environment variables:
export LIBTORCH=`pwd`/libs/libtorch
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/libs/libtorch/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}3. Datasets 📁
Create the data directory:
mkdir dataNow let’s download the MNIST datasets:
curl -L "http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz" > data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
curl -L "http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz" > data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
curl -L "http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz" > data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
curl -L "http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz" > data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gzUnzip all files:
gunzip data/*.gz4. Build and Running 🚀
Now just run the command below to build and run the project:
cargo build && cargo run
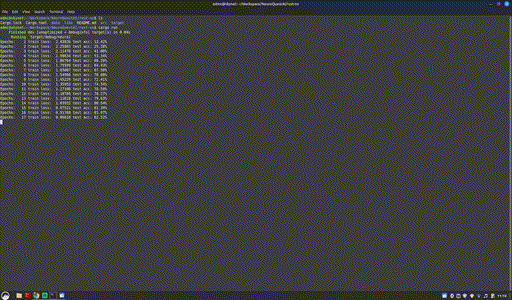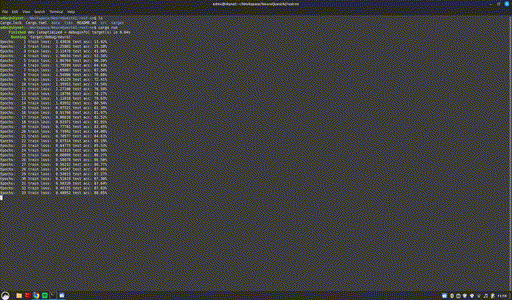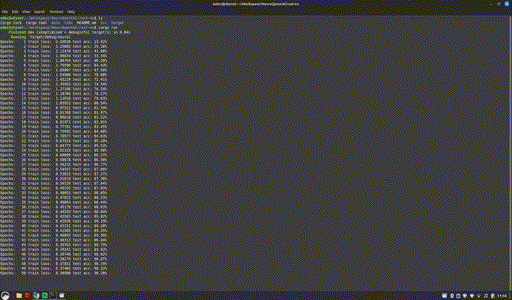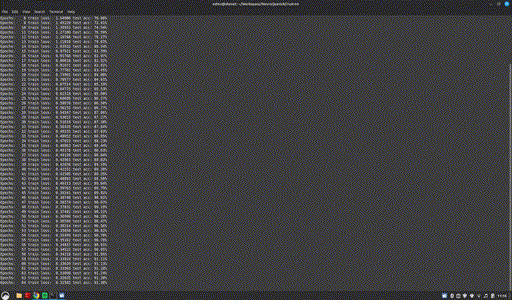
Project page: https://github.com/NeuroQuestAi/rust-nn
